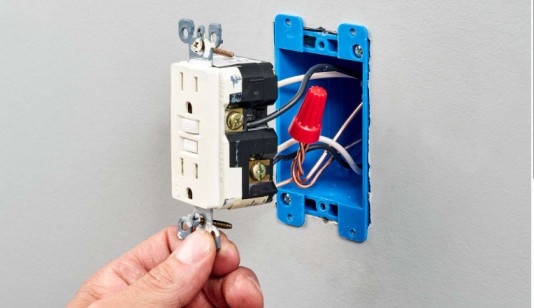
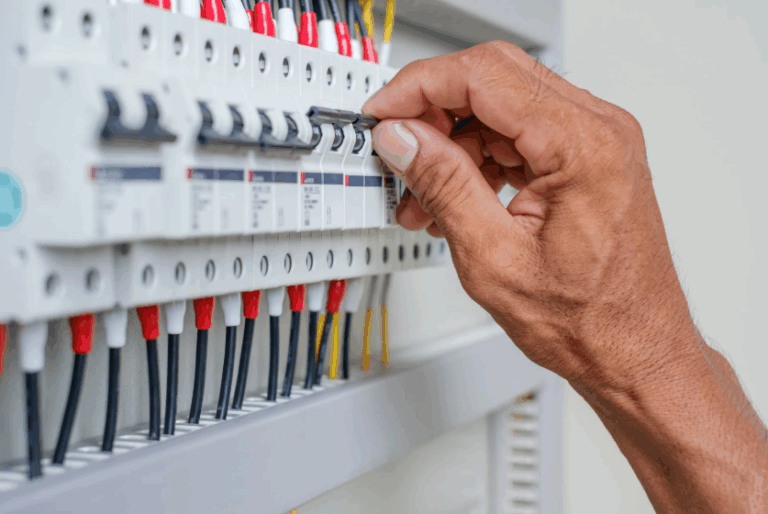
Electrical outlet wiring is a fundamental part of any home or commercial building’s electrical system. If you’re upgrading existing outlets or installing new ones, ensuring safety and compliance with local codes is crucial. This guide will walk you through the essential steps for safe, effective outlet wiring installation in Toronto, including safety precautions, types of outlets, and troubleshooting tips.
What is Outlet Electrical Wiring?
Outlet electrical wiring connects electrical outlets (receptacles) to the electrical grid, facilitating the flow of electricity to power devices. Residential systems typically operate on 120V circuits, while more powerful appliances might require 240V. Proper installation involves assessing your system’s specific needs, such as:
- Circuit Capacity
- Wire Gauge
- Outlet Type
Types of Electrical Outlets
- Standard 120V Outlets: The most common, used for general appliances.
- High-Power 240V Outlets: Necessary for appliances like dryers or air conditioners.
- USB Outlets: For charging mobile devices without a separate adapter.
- Smart Outlets: Enable remote control, energy monitoring, and integration with smart home systems.
Wiring Methods
- Romex (Non-Metallic Sheathed Cable): A common choice in residential wiring, housing all three wires (hot, neutral, and ground) in a single sheath.
- Conduit Wiring: Used in industrial settings or areas requiring extra protection, with wires running through metal or plastic tubes.
- Direct Burial: Wires buried underground for outdoor setups.
Key Components of Outlet Wiring
- Hot Wire (Live): Transports electricity from the power source (typically black or red).
- Neutral Wire: Carries electricity back to the source (usually white).
- Ground Wire: Directs electricity safely to the earth in case of faults (typically green or bare copper).
Outlets:
- Standard Outlets: Used in most areas for standard devices.
- GFCI Outlets: Required in wet areas (like bathrooms or kitchens) to protect against electrical shock.
- Specialized Outlets: For heavy-duty appliances like ovens or dryers.
Circuit Breakers/Fuses:
Prevent electrical overload by shutting off the power during fault conditions.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
- Turn Off Power: Always cut the power by switching off the circuit breaker to prevent accidents.
- Remove Old Outlet: Unscrew and carefully detach the old outlet.
- Inspect Wiring: Check for wear and tear or damage.
- Connect New Outlet: Attach the wires to the corresponding terminals on the new outlet.
- Secure Outlet: Fix the outlet securely back into the electrical box.
- Restore Power and Test: Turn the circuit breaker back on and test the outlet with a voltage tester.
Common Issues in Outlet Wiring
- Tripped Breakers: Occurs when the circuit is overloaded. Overloaded circuits may require a higher-capacity outlet.
- Loose Connections: Can cause overheating or sparking. Tighten all connections during installation.
- GFCI Outlet Issues: Frequently tripping GFCIs may indicate wiring faults or that the outlet needs replacement.
Safety Considerations
- GFCI Outlets: Install these in wet areas to reduce the risk of electrical shock.
- AFCI Breakers: These breakers help prevent fires caused by arcing faults in the wiring.
- Regular Inspections: Inspect outlets for signs of wear, discoloration, or unusual smells that might indicate a problem.
Compliance with Ontario Electrical Safety Code
In Toronto, all electrical work must adhere to the Ontario Electrical Safety Code (OESC). Always ensure that your installation meets these safety standards. Additionally, work may require permits and inspections, depending on the complexity of the installation.
Energy Efficiency and Smart Outlets
- Energy-Efficient Outlets: Some modern outlets feature built-in energy-saving features, like timers or automated turn-offs.
- Smart Outlets: These can help monitor and control energy use remotely. They also integrate with smart home systems, such as Amazon Alexa and Google Home.
When to Consult a Professional
While DIY installations are possible, consider consulting a licensed electrician for:
- Complex installations or upgrades
- Troubleshooting persistent electrical issues
- Ensuring compliance with the Ontario Electrical Safety Code
Conclusion
Proper installation of outlet wiring is crucial for both safety and functionality in your home. By following these guidelines and understanding the key components, you’ll ensure your electrical system operates effectively and safely. When in doubt, always seek professional help to avoid risks and comply with safety regulations.
FAQ
What is the maximum distance between electrical outlets?
Outlets should be installed so that no point along the floor line is more than 6 feet (1829 mm) from a receptacle, ensuring easy access.
What is the 2-4 outlet rule?
The 2-4 rule applies to kitchen countertops. No point should be more than 24 inches from an outlet, and outlets should be spaced no more than 48 inches apart.
What is the code height for electrical outlets?
Electrical outlets are typically installed 12 inches (305 mm) from the floor to the bottom of the receptacle box.
How far should outlets be from a door?
Outlets must be no more than 6 feet from a door on an interior wall, with some exceptions for small wall sections.
How many outlets can be on a 20-amp circuit?
A 20-amp circuit can typically support about 10 outlets, assuming each outlet draws a maximum of 1.5 amps.